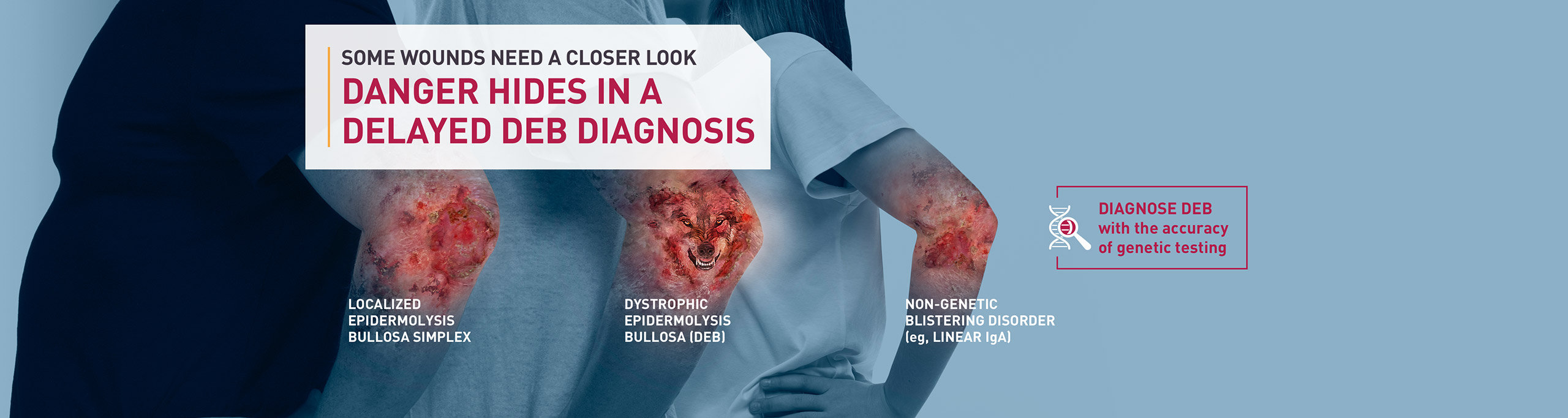
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is a serious genetic blistering disorder.1-4
DEB is caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, resulting in lack of functional collagen VII, driving fragile skin, mucosa, and epithelial linings. Symptoms can include blistering, wounds, scarring, and nail, oral, and GI abnormalities.
Serious consequences can include:
- Internal complications
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- Early mortality
Understanding DEB
DEB is a serious genetic blistering disorder caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene1,2
Risks with DEB
DEB has unique risks and complications that require proactive care9-11
References: 1. Fortuna G, Aria M, Cepeda-Valdes R, Trevino MGM, Salas-Alanís JC. Pain in patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: association with anxiety and depression. Psychiatry Investig. 2017;14(6):746-753. doi:10.4306/pi.2017.14.6.746 2. Eichstadt S, Tang JY, Solis DC, et al. From clinical phenotype to genotypic modelling: incidence and prevalence of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB). Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:933-942. doi:10.2147/CCID.S232547 3. Fine J-D, Mellerio JE. Extracutaneous manifestations and complications of inherited epidermolysis bullosa: part I. Epithelial associated tissues. JAMA Dermatol. 2009;61:367-384. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.03.052 4. DEBRA International. Dystrophic EB. Accessed June 13, 2022. https://www.debra-international.org/dystrophic-eb 5. Has C, Liu L, Bolling MC, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for laboratory diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182(3):574-592. doi:10.1111/bjd.18128 6. Kao C-H, Chen S-J, Hwang B, Yang A-H, Hsu C-Y, Huang C-H. Junctional epidermolysis bullosa. J Chin Med Assoc. 2006;69(10):503-506. doi:10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70318-1 7. Tabor A, Pergolizzi JV Jr, Marti G, Harmon J, Cohen B, Lequang JA. Raising awareness among healthcare providers about epidermolysis bullosa and advancing toward a cure. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017;10(5):36-48. 8. Bruckner AL, Losow M, Wisk J, et al. The challenges of living with and managing epidermolysis bullosa: insights from patients and caregivers. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020;15(1):1. doi:10.1186/s13023-019-1279-y 9. Christiano AM, Crollick J, Pincus S, Uitto J. Squamous cell carcinoma in a family with dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: a molecular genetic study. Exp Dermatol. 1999;8(2):146-152. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.1999.tb00364.x 10. Denyer J, Pillay E, Clapham J. Best practice guidelines for skin and wound care in epidermolysis bullosa 2017. Wounds International. May 3, 2017. Accessed June 13, 2022. https://www.woundsinternational.com/resources/details/best-practice-guidelines-skin-and-wound-care-in-epidermolysis-bullosa. 11. Fine J-D, Johnson LB, Weiner M, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa and the risk of life-threatening cancers: the National EB Registry experience, 1986-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(2):203-211.